Alaska Blind Child Discovery
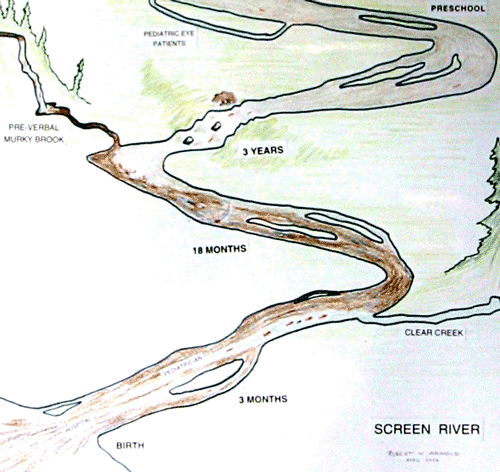
Screen River pre-School
Home
Amblyopia
is an evolving disease for which a series of age-appropriate public
health screening is valid
and cost-effective. These screening
tests are well-deliverable during scheduled, well-child health screenings
described by the American Academy
of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines. Unfortunately, not every child benefits
from consistent AAP guideline vision screening due to issues of health
insurance coverage, pediatrician availability, experience and compliance,
or attendance at public health alternatives to pediatrician’s offices.
In a normal child, vision, and specifically
acuity, improves over time as a result of brain learning.
Amblyopia is subnormal brain learning of vision during the first decade
of life.
ABCD draws an analogy between
pediatric vision screening and attempts to catch
the elusive, choicest Alaskan salmon in a spawning stream.
Salmon? Salmon enter their original spawning stream bright and fresh from the ocean. They may swim in the main channel, or through smaller tributaries. As they enter the murky river, some swim through areas of clearer water mixing in. As they proceed up-river, some continue to feed and grow, while others gradually waste. In the braided river, large and small salmon may swim, or pool-up in various braided channels so that a concerted effort on only one channel will miss some of them. An observant bear might pluck some of the choicest salmon from the stream. Fisherman have a choice of various methods of fishing, from a tiny, selective dry fly, to a gill-net with specific mesh size and thread color, to the “kill-anything-that-swims” Dupont-spinner dynamite that will catch not only choice salmon, but also any other non-desirable inhabitant of the river. Further up-river, the salmon follow their pre-determined course to various spawning beds in different feeding lakes.
ABCD History
Kids Eye Disorders
Amblyopia
Vision Screening
Evolving Process: There are several risk factors for amblyopia, namely strabismus (misaligned eyes), refractive (poor focus in one or both eyes) and deprivation (blocking light such as pediatric cataract). Over the course of childhood, some children will have a positive amblyopia risk factor the entire decade while others may possess poor focus one year, but be better focused the next.
Age at Screening: Infants are just beginning to learn vision whereas older children either have gained semi-permanent good acuity, or have semi-permanent, refractory amblyopia. Salmon enter the spawning river bright and fresh from the ocean, but then commence a degrading process leading to being “spawned out” and death when they have completed their task in the spawning bed.
Location of screening: Screening may occur in the hospital and in the pediatrician’s office by AAP guidelines, but may also take place in public health or family medicine clinics, in community charitable outreaches, in preschools, in HeadStart programs and in schools. Some children with amblyopia are detected during an inadvertent eye exam or following trauma. Not all children attend pre-school or Headstart. The majority of students are educated in public schools, however many others attend private schools or are home schooled.
Method of screening: Early screening relies on objective measures while older children are able to submit subjective testing of acuity. Some children with amblyopia are observed by parents and caregivers due to symptoms, warning signs or strabismus.
Issues
ABCD Clinics
References
Contact ABCD
Birth: Red-Reflex: Most children are born in the hospital, but others are born in birthing centers or at home. AAP recommends that all newborns have red reflex testing and observation particularly to detect congenital cataract.
Infant: 3-4 months: Fixation, cover test: AAP recommends that the fixation of each eye independently and the alignment of the eyes by cover test and version testing be done to detect early strabismic amblyopia
Brückner Testing can be performed in infants to detect leukocoria, high refractive error, strabismus.
Toddler: Objective Testing: photoscreening, remote autorefraction and Brückner testing can detect refractive and strabismic amblyopia as well as medic opacities such as cataract.
Pre-K Acuity testing: 3-4 year olds can identify by verbalization or matching surround, optotypes acuity, with monocularity assured by patching with referral less than 20/40.
Warning Signs: white pupil, red eye, pain, swelling, misalignment, nystagmus, abnormal pupils, head tilt/turn, excess tearing, large eye, moving too close, lack of fixation, light sensitivity, droopy lid, headache, excess blinking.