Alaska Blind Child Discovery
Nasolacrimal Care: PEDIG
Home
ABCD History
Kids Eye Disorders
Amblyopia
Vision Screening
Issues
ABCD Clinics
References
Contact ABCD
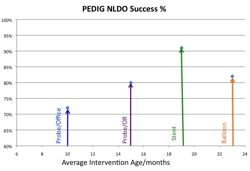
PEDIG, Repka MX, Chandler DL, et al. Primary treatment of nasolacrimal duct obstruction with probing in children younger than 4 years. Ophthalmology. Mar 2008;115(3):577-584 e573. * OBJECTIVE: To report the outcome of nasolacrimal duct probing as the primary treatment of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO) in children younger than 4 years. DESIGN: Prospective nonrandomized observational multicenter study (44 sites). PARTICIPANTS: Nine hundred fifty-five eyes of 718 children 6 to <48 months old at the time of surgery with no prior nasolacrimal surgical procedure and with at least one of the following clinical signs of NLDO present: epiphora, mucous discharge, and increased tear lake. INTERVENTION: Probing of the nasolacrimal system of the affected eye. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURE: Treatment success was defined as no epiphora, mucous discharge, or increased tear lake present at the outcome visit 1 month after surgery. RESULTS: Proportions of eyes treated successfully were 78% (95% confidence interval [CI], 75%-81%) overall, 78% for the 421 eyes in children 6 to <12 months old, 79% for the 421 eyes in children 12 to <24 months, 79% for the 37 eyes in children 24 to <36 months, and 56% for the 11 eyes in children 36 to <48 months. The probability of treatment success was lower in eyes operated in an office setting than in eyes operated in a surgical facility (adjusted relative risk, 0.88 [95% CI, 0.80-0.96]), with success reported in 72% (95% CI, 66%-78%) of probings performed in an office and 80% (95% CI, 77%-84%) of probings performed in a facility. The probability of treatment success was also lower in eyes of patients with bilateral disease (adjusted relative risk, 0.88 [95% CI, 0.81-0.95]). CONCLUSIONS: In children 6 to <36 months old, probing is a successful primary treatment of NLDO in about three fourths of cases, with no decline in treatment success with increasing age. The study enrolled too few children ages 36 to <48 months to allow a conclusion regarding the probability of treatment success in this age group.
PEDIG, Repka MX, Melia BM, et al. Primary treatment of nasolacrimal duct obstruction with balloon catheter dilation in children younger than 4 years of age. J AAPOS. Oct 2008;12(5):451-455. * PURPOSE: To report the outcome of nasolacrimal duct balloon catheter dilation as the primary treatment of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO) in children younger than 4 years of age. METHODS: One hundred two children (151 eyes) ages 12 to <48 months (mean, 23 months) at the time of surgery, who previously had not undergone a nasolacrimal surgical procedure and who presented with at least one of the following clinical signs of NLDO--epiphora, increased tear lake, and/or mucous discharge--were enrolled in a prospective, nonrandomized observational multicenter study (20 sites). All children received balloon catheter dilation of the nasolacrimal system of the affected eye(s). RESULTS: Treatment success was defined as no epiphora, increased tear lake, and/or mucous discharge present at the outcome visit at 1 month after surgery. The proportion of eyes treated successfully was 82% (95% CI: 74%-88%). The dye disappearance test at outcome was normal in 105 (73%), indeterminate in 15 (10%), and abnormal in 23 (16%) of the 143 eyes tested. CONCLUSIONS: In children 12 to <48 months of age, balloon catheter dilation as a primary treatment of NLDO was successful in approximately 80% of cases. Because we did not perform a randomized trial with a comparison group, we were unable to determine how this procedure's success rate compares with that of simple probing or nasolacrimal intubation in this age group.
PEDIG, Repka MX, Melia BM, et al. Primary treatment of nasolacrimal duct obstruction with nasolacrimal duct intubation in children younger than 4 years of age. J AAPOS. Oct 2008;12(5):445-450. * PURPOSE: To report the outcome of nasolacrimal duct intubation as the primary treatment of congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction (NLDO) in children younger than 4 years of age. METHODS: A total of 182 eyes of 139 children receiving intubation with planned tube retention for 2 to 5 months were enrolled in a prospective, nonrandomized observational multicenter study (19 sites). Children were ages 6 months to <45 months at the time of surgery, with no previous nasolacrimal surgical procedures and had at least one of the following clinical signs of NLDO: epiphora, mucous discharge, and/or increased tear lake. RESULTS: Treatment success was defined as absence of epiphora, mucous discharge, and increased tear lake at the outcome visit, 1 month after tube removal. The surgical outcome was assessed in 150 eyes (82% of cohort). The proportion of eyes treated successfully was 91% (95% CI: 86%-95%). The outcome dye disappearance test was normal in 125 (86%) eyes, indeterminate in 13 (9%), and abnormal in 7 (5%) of the 145 eyes tested. Monocanalicular tubes were used in 74% of cases. The tube was removed before the planned minimum retention time of 2 months in 61 eyes (41%). For 23 eyes, the early removal was attributed to inadvertent displacement by the patient. CONCLUSIONS: In children 6 months to <45 months of age, nasolacrimal duct intubation in a nonrandomized and noncomparative trial was a successful primary treatment of NLDO in about 90% of cases not lost to follow-up.
PEDIG, Repka MX, Chandler DL, et al. NLD-2: Balloon catheter dilation and nasolacrimal duct intubation for treatment of nasolacrimal duct obstruction after failed probing. Arch Ophthalmol 2009;127(5):633-9. OBJECTIVE: To compare the outcomes of balloon catheter dilation and nasolacrimal intubation as treatment for congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction after failed probing in children younger than 4 years. METHODS: We conducted a prospective, nonrandomized, multicenter study that enrolled 159 children aged 6 months to younger than 48 months who had a history of a single failed nasolacrimal duct probing and at least 1 of the following clinical signs of nasolacrimal duct obstruction: epiphora, mucous discharge, or increased tear lake. One hundred ninety-nine eyes underwent either balloon catheter nasolacrimal duct dilation or nasolacrimal duct intubation. Treatment success was defined as absence of epiphora, mucous discharge, or increased tear lake at the outcome visit 6 months after surgery. RESULTS: Treatment success was reported in 65 of 84 eyes (77%; 95% confidence interval, 65%-85%) in the balloon catheter dilation group compared with 72 of 88 eyes (84% after adjustment for intereye correlation; 74%-91%) in the nasolacrimal intubation group (risk ratio for success for intubation vs balloon dilation, 1.08; 0.95-1.22). CONCLUSION: Both balloon catheter dilation and nasolacrimal duct intubation alleviate the clinical signs of persistent nasolacrimal duct obstruction in a similar percentage of patients.